First aid - CPR, heart attack, and stroke
2024-06-28
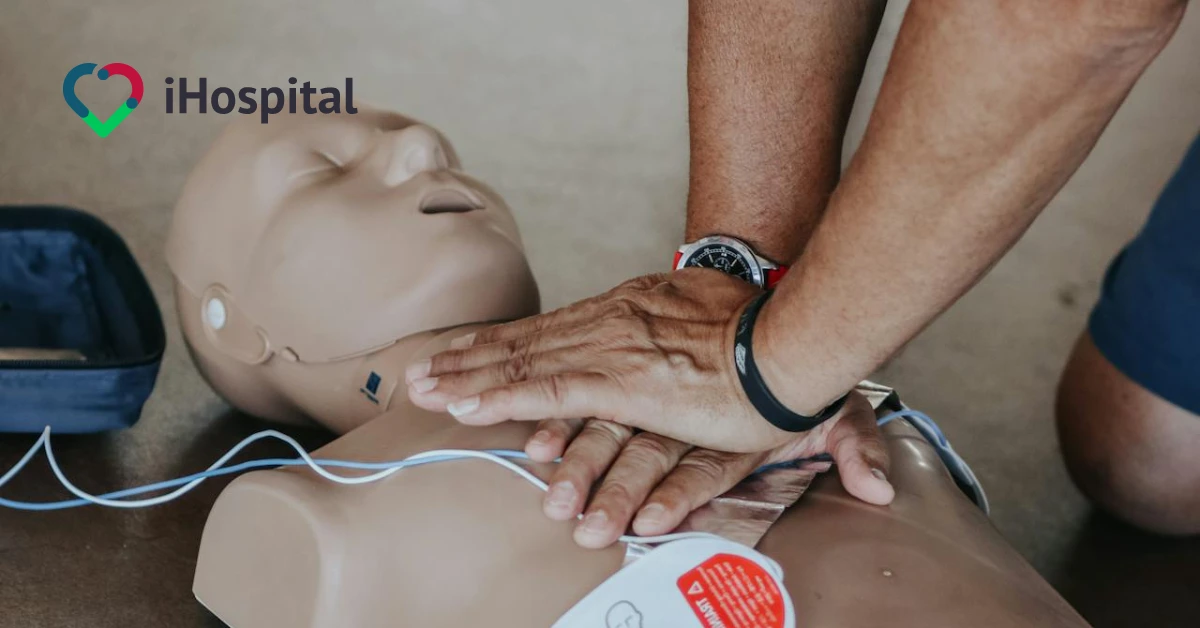
<h1>First aid - CPR, heart attack, and stroke</h1><p> </p><p>How many times have you found yourself in a situation where you needed to save someone's life? Armed with basic first aid skills can make a crucial difference in such unpredictable situations, it not only helps you save the lives of others but also your own. Whether it's a minor injury or a life-threatening condition, knowing what to do in those crucial first moments can determine the outcome, it can be the difference between life and death, so it's essential to always be prepared.</p><p>Learn the ABCs of first aid, how to perform CPR, and what first aid skills for both stroke and heart attack (stroke) everyone should have.</p><h2>The ABCs of First Aid</h2><ol><li>Before providing assistance, stay calm and make sure you and the environment are safe from any potential danger, and ask for help from others at the same time.</li><li>If the casualty is unconscious, check for breathing and pulse, and try to wake them up by shaking their shoulders and calling out loudly and close to their ears.</li><li>If there is no response (breathing/pulse), <strong>call 911 and immediately start CPR</strong> (listed below).</li><li>If the patient is unconscious but breathing and pulse, place them in the <strong>recovery position</strong> (described below) until help arrives.</li></ol><h2>Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)</h2><p><a href="https://youtu.be/1w_gVVaccVs?si=evygD8rpS9oFwHk5" target="_blank">https://youtu.be/1w_gVVaccVs?si=evygD8rpS9oFwHk5</a><br></p><p>1. The 3 most important actions to perform when performing CPR are summarized in <strong>ABC:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Airway:</strong> If the person is not breathing, open the airway by lifting the person's head.</li><li><strong>Breathing:</strong> If you open the airway without success, provide rescue breathing.</li><li><strong>Circulation:</strong> While performing rescue breathing, press down hard and fast in the center of the person's chest, using both hands. You may hear a pop or crackle; this is normal.</li><li>Try 30 chest compressions, then give two rescue breaths, and repeat until the pulse is restored. Do about 100 to 120 compressions per minute.</li></ul><p>2. Use an AED if one is available, but don't leave CPR until you find one.</p><p>3. Continue resuscitation until an ambulance arrives, or the patient regains consciousness, breathing, and pulse.</p><p>4. If the patient regains breathing but remains unconscious, place the patient in the recovery position (below) until help arrives.</p><h2>Awakening position</h2><p><a href="https://youtu.be/qdYbKpdPxCs?si=PmjiwLD1hYJC29ov" target="_blank">https://youtu.be/qdYbKpdPxCs?si=PmjiwLD1hYJC29ov</a><br></p><p>The awake position is suitable for a person who is <strong>unconscious</strong>, but <strong>breathing normally</strong> and has a pulse:</p><ul><li>Place the patient in a supine position on the floor.</li><li>Sit next to the patient on your knees.</li><li>Straighten the patient's legs.</li><li>Take the hand of the patient closest to you and hold it at a straight angle to the side of the head.</li><li>Take the other hand, open the palm, and place it on the cheek on the side closest to you.</li><li>Lift the leg of the patient furthest away from you to create an angle.</li><li>Tilt the patient's entire torso toward you, with the open palm resting on the patient's cheek.</li><li>Lift the patient's chin and tilt the head back slightly to open the airway, making sure there is no obstruction.</li><li>Monitor the airway and breathing until medical help arrives, by noticing the release of air, chest movement, or the sound of breathing.</li></ul><h2>First aid for stroke</h2><p>Stroke requires urgent medical care, here's how to administer first aid for stroke.</p><p><a href="https://youtu.be/OyucxzOWG3k?si=zKxnEOuUv353JOYs" target="_blank">https://youtu.be/OyucxzOWG3k?si=zKxnEOuUv353JOYs</a><br></p><h3>The first step: Recognize the signs of a stroke</h3><p>Use the acronym <strong>FAST</strong> to help you remember the most prominent signs:</p><ul><li><strong>Face:</strong> Is one side of the face drooping?</li><li><strong>Arm:</strong> Is there weakness in one arm?</li><li><strong>Speech</strong>: Is there difficulty speaking or understanding speech?</li><li><strong>Time</strong>: If the answer to any of the above is yes, <strong>call 911 immediately</strong>, the sooner you call for help, the better the patient's chances of a good recovery.</li></ul><h3>Second Step: Provide first aid</h3><ul><li><strong>Keep the patient calm:</strong> Reassure the patient and tell them that help is on the way.</li><li><strong>Place the patient in a comfortable position:</strong> Either sitting or lying on their side, with their head and shoulders slightly elevated with a pillow or piece of clothing underneath.</li><li><strong>Loosen tight clothing:</strong> Release any tight clothing around the patient's neck or chest.</li><li><strong>Cover the patient if they are cold:</strong> Use a blanket or coat to keep them warm.</li><li><strong>Monitor the patient's vital signs:</strong> Monitor the patient's breathing, pulse, and consciousness regularly until the ambulance arrives.</li><li><strong>Do not give the patient anything to drink or eat:</strong> This can cause choking if the patient is unconscious or has difficulty swallowing.</li><li><strong>Do not move the patient if there are head or neck injuries:</strong> Wait for paramedics to arrive.</li><li><strong>Watch out for other signs of stroke:</strong><ul><li>Weakness and numbness on one side of the body.</li><li>Difficulty understanding what others are saying.</li><li>Drooling or difficulty swallowing.</li><li>Trouble seeing.</li><li>Sudden, severe headache.</li><li>Dizziness or loss of balance.</li><li>Confusion.</li><li>Loss of responsiveness.</li></ul></li><li><strong>If the person is unconscious but breathing:</strong> Place them in the recovery position (described above).</li><li><strong>If the person is unconscious and not breathing:</strong> Start cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).</li></ul><h4>Important notes:</h4><ul><li><strong>Seek emergency medical care even if your symptoms last only a few minutes or hours:</strong> This could be a sign of a mini-stroke, or transient ischemic attack (TIA), which can serve as a warning of a major stroke to come.</li><li><strong>Don't give the patient any medications:</strong> Medications may interact with other medications the patient is taking or worsen the patient's condition.</li><li><strong>Record the time when the stroke symptoms first appeared:</strong> This information will help the doctor better identify and treat the type of stroke.</li></ul><h2>First aid for a heart attack (clot)</h2><p>A heart attack/clot requires urgent medical intervention, here's how to administer first aid for a clot.</p><p><a href="https://youtu.be/ZnskQFRviV4?si=8uaDWdCD0mYDDZ27" target="_blank">https://youtu.be/ZnskQFRviV4?si=8uaDWdCD0mYDDZ27</a><br></p><h3>First step: Recognize the signs of a heart attack/clot</h3><ul><li>Chest pain that may feel like pressure, tightness, tenderness, squeezing, or pain.</li><li>Pain or discomfort that spreads to the shoulder, arm, back, neck, jaw, teeth, or sometimes the upper abdomen.</li><li>Cold sweating.</li><li>Fatigue.</li><li>Heartburn or indigestion.</li><li>Dizziness or sudden lightheadedness.</li><li>Nausea.</li><li>Shortness of breath.</li></ul><h3>Second Step: Act quickly:</h3><ul><li><strong>Call 911 or your local emergency number:</strong> Every second counts during a heart attack. The sooner you call for help, the better your chances of recovery.</li><li><strong>Place the patient in a comfortable position:</strong> The best position is to sit on the floor, with knees bent and head and shoulders propped up against a wall or something.</li><li><strong>Give him or her an aspirin to chew:</strong> Aspirin may help prevent blood clots and dissolve the blood clot that causes a heart attack, make sure he is not allergic to aspirin and is older than 16 years old.</li><li><strong>Give him his seizure medications if he is on them:</strong> Give a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue (sublingual pill) if previously prescribed by a doctor.</li><li><strong>If the person has no pulse or is not breathing:</strong> Start CPR.</li><li><strong>Find an automated external defibrillator (AED):</strong> This device may help restore a normal heart rhythm in the event of a cardiac arrest.</li></ul><h3>Step three: Help the patient:</h3><ul><li><strong>Loosen tight clothing:</strong> Remove any clothing that is pressing on the patient's neck or chest.</li><li><strong>Reassure the patient:</strong> Remain calm and reassure the patient that help is on the way.</li><li><strong>Monitor the patient's vital signs:</strong> Monitor the patient's breathing and pulse regularly until medical help arrives.</li><li><strong>Do not offer them drinks or food:</strong> This can cause choking if the patient is unconscious or has difficulty swallowing.</li><li><strong>Do not move the patient if they have a head or neck injury:</strong> Wait for paramedics to arrive.</li></ul><h4>Important notes:</h4><ul><li><strong>Do not give the patient any other medications:</strong> To avoid drug interactions with aspirin, nitroglycerin, or other medications the patient is taking, or to avoid worsening the condition.</li><li><strong>Record the time when the symptoms of the heart attack first appeared:</strong> This information will help your doctor better identify and treat the type of heart attack.</li></ul><p>It is advisable for everyone to take an accredited first aid course from a specialized organization to gain hands-on experience in dealing with emergencies and practice these skills.</p><p><strong>Are you looking for exceptional healthcare that caters to your individual needs?</strong></p><p><strong>With iHospital, you get:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Patient-centered care: We put your health first and understand your individual needs.</strong></li><li><strong>Experienced physicians: We have an extensive network of skilled physicians with expertise in all medical specialties.</strong></li><li><strong>Flexible appointments: We offer flexible appointments to suit your needs, including evening and weekend hours, home visits, and telemedicine.</strong></li><li><b>Comprehensive care: We offer a wide range of medical services, including general medicine, pediatrics, preventive care, surgery, and more.</b></li></ul><p><strong>Don't wait any longer! <a href="https://www.ihospitalapp.com/ar/doctor-profile/1154_%D8%A3%D8%B7%D8%A8%D8%A7%D8%A1-%D8%A2%D9%8A-%D9%87%D9%88%D8%B3%D8%A8%D9%8A%D8%AA%D8%A7%D9%84-Specialist-Doctors-Home-Visit">Call us now</a> and get the care you deserve.</strong></p><hr><h2>References</h2><ol><li aria-level="1"><a href="https://cpr.heart.org/en/resources/what-is-cpr">What is CPR</a>, American Heart Association CPR & First Aid</li><li aria-level="1"><a href="https://www.sja.org.uk/get-advice/first-aid-advice/stroke/">Stroke - Warning Signs & First Aid Advice</a>, St John Ambulance</li><li aria-level="1"><a href="https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319007">First aid for stroke: What do you do?</a>, Medical News Today</li><li aria-level="1"><a href="https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-heart-attack/basics/art-20056679">Heart attack: First aid</a>, Mayo Clinic</li><li aria-level="1"><a href="https://www.sja.org.uk/get-advice/first-aid-advice/heart-conditions/heart-attack/">Heart Attack - Signs, Symptoms, & What to do</a>, St John Ambulance</li></ol>